Purified FAb + F(Ab’)2 Fragments
Leverage the many benefits of fragment generation
So, is it really worth the effort?
Due to low yields, highly inconsistent results (across various species and isotypes) and questions about practical applicability, that question frequently accompanies discussions around traditional FAb and F(Ab’)2 fragment production.
Relying on pepsin and papain for fragment generation frequently requires extensive optimization . . . and even then, purity might be low and the antigen-binding activity of the antibody can be compromised. Fragment generation from different species and isotypes often requires specialized procedures with a steep learning curve and a wide range of production and analysis techniques.
In short, it’s commonly been a high-effort activity for an uncertain outcome.
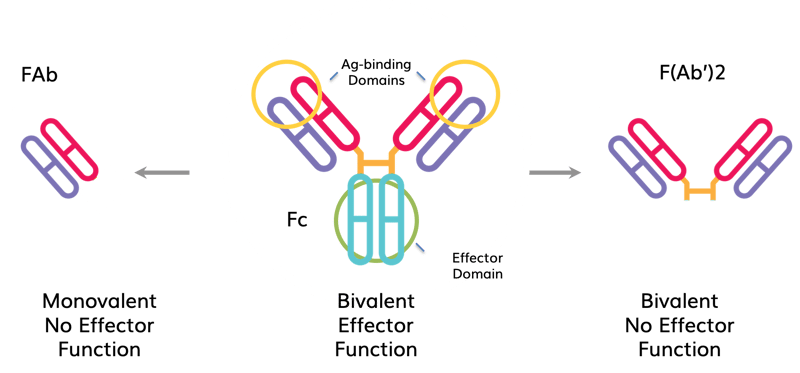
| Characteristics of whole IgG and its FAb and F(Ab’)2 fragments. Whole IgG molecules are composed of two Ag-binding domains (FAb) and one effector domain (Fc). Cleavage with the appropriate enzymes can create either an FAb (left) or 2 FAbs joined by a disulfide bond (e.g., F(Ab’)2, right). FAb’s and F(Ab’)2s have one and two Ag binding domains, respectively. Neither has the Fc domain that mediates Ab effector function such as Fc receptor binding, complement-mediated cytotoxicity or Ab-dependent cellular cytotoxicity (ADCC). |
Yet recent reagent enzyme advances and other tools have enabled skilled antibody researchers to generate purified antibody fragments that can be put to wide use. Possible applications of FAb and F(Ab')2 fragments vary greatly. They can be used as an antigen, a characterization tool, an antibody detection or delivery tool as well as a manufacturing tool.
Producing true specificity of cleavage — yielding a functional antigen-binding domain or effector domain — is today a more streamlined and cost-effective exercise, allowing more researchers to take advantage of these applications.
| Common Applications of FAb and F(Ab')2 Fragments | ||||
| Purpose | FAb | F(Ab')2 | Application Area | Advantages |
| Anti-idiotype Ab generation | Best | Y | Antigen preparation | Improved immunogenicity |
| Removal of Fc from Fc fusion protein | Y | Y | Antigen preparation | Improved immunogenicity |
| Ab or Ab/Ag crystal structure | Best | Y | Antibody characterization | Improved structure resolution |
| Monovalent binding analysis — Affinity | Y | N | Antibody characterization | Free of avidity effects |
| Monovalent binding analysis — Epitope | Y | N | Antibody characterization | Binding free of steric hindrance |
| Creation of bi-specifics from candidate IgGs | Y | N | Antibody characterization and delivery | Non-recombinant method |
| Eliminate Fc-mediated effector functions | Y | Y | Antibody characterization and delivery | Discern Ag binding vs. effector function |
| Enhance tissue penetration | Best | Better | Antibody characterization and delivery | Improved Ag binding and detection |
| Greater sensitivity in assays | Best | Better | Antibody delivery and detection | Reduce steric hindrance |
| Abrogate anti-Fc antibody detection | Y | Y | Antibody detection | Reduced non-specific binding |
| Abrogate binding to protein A or G | Y | Y | Antibody detection | Control of Fc binding by secondary reagents |
| Domain characterization | Y | Y | Therapeutic antibody manufacturing | Product identity |
| Isoform and glycoform analysis | Y | Y | Therapeutic antibody manufacturing | Product identity |
Our project management team can help you determine when the use of a FAb or F(Ab’)2 is a good fit for your specific research needs. And if your initiative calls for it, we can help you create and quality-check purified fragments for a variety of antibody species and isotypes.
| FAb and F(Ab')2 digestions offered by Antibody Solutions |
|
| SPECIES | ISOTYPES |
| HUMAN | IgG1, IgG2, IgG3, IgG4 |
| MOUSE | IgG1, IgG2a, IgG2b, IgG2c, IgG3 |
| RAT | IgG1, IgG2a, IgG2b, IgG2c |
| OTHER SPECIES | Various IgG – Let's talk about your specific needs. |
True to our fit-for-purpose philosophy, we tailor our methodology to your target molecule. We help you take advantage of:
- Time savings through enzyme-cleavage site-specific reagents that can bind uniquely to the FAb and F(Ab’)2 fragments, purifying the fragment in a single step
- Opportunities to better measure monovalent vs. divalent binding to an antigen to characterize affinity, avidity, and epitope specificity. This may be especially useful for anti-idiotype antibody development, tissue penetration studies, therapeutic Ab manufacturing applications, etc.
- The confidence that comes from applying our experience and expertise in digestion (Step One) and purification (Step Two) in equal measures
- The certainty that comes from quality control measures, including non-reduced SDS-page gel testing, that confirm successful purification of FAb and F(Ab’)2 fragments, including non-reduced SDS-gel electrophoresis
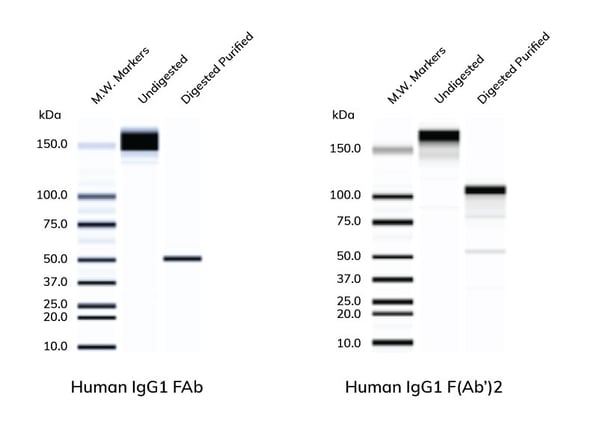
| Non-reduced SDS-gels of whole IgG1 or affinity purified human IgG FAb (left) & F(Ab')2 (right). Whole human IgG was digested with the appropriate enzymes of FAb or F(Ab')2 and the fragments were then affinity purified from the digestion mixture. Appropriate molecular weights for the two fragments were obtained. Results may vary by species and isotype of the Ab. |
The many uses and advantages of fragment generation are rapidly becoming clear, and we’re ready to help you capitalize on them to advance your discovery. With Antibody Solutions at your side, you won’t have to devote precious time and resources to building an in-house fragment-generation capability for an “every-now-and-then” need.
Contact us today to get the conversation started.

