Purified fAb + f(Ab')2 Fragments
Fabricating your Project
Over the last couple of decades, the advantages of antibody fragment generation have become clear. They can be used as an antigen, a characterization tool, an antibody detection or delivery tool, and even as a manufacturing tool. Because FAb and F(Ab’)2 have so many applications, knowing when and where they’re best used is more important than ever.
Characteristics of whole IgG and its FAb and F(Ab’)2 fragments. Whole IgG molecules are composed of two Ag-binding domains (FAb) and one effector domain (Fc). Cleavage with the appropriate enzymes can create either an FAb (left) or 2 FAbs joined by a disulfide bond (e.g., F(Ab’)2, right). FAbs and F(Ab’)2s have one and two Ag binding domains, respectively. Neither has the Fc domain that mediates Ab effector function such as Fc receptor binding, complement-mediated cytotoxicity or Ab-dependent cellular cytotoxicity (ADCC).
Optimizing FAb and Fragment Selection
Most of the FAb fragments we develop are part of larger antibody discovery projects. This is especially the case for customers who are looking to produce anti-idiotypic antibodies to their drug. Our project management team can help you determine when the use of a FAb or F(Ab’)2 is a good fit for your specific research needs.
No matching results found.
Producing true site-specific cleavage — yielding a functional antigen-binding domain or effector domain — has become a more streamlined and cost-effective exercise than traditional pepsin or papin approaches. This allows more researchers to take advantage of the above applications.
Because working with Fabs and F(Ab’)2s can be a bit of a minefield for the unfamiliar, great peace of mind can come from handing off this difficult task to a more experienced pair of hands. We’re happy to be that pair of hands: Taking advantage of our FAb and F(Ab’)2 offerings mean you won’t have to devote precious time and resources to building an in-house fragment-generation capability for an “every-now-and-then” need.
A Full Array of FAb and F(Ab')2 Digestions
Our project management team can help you determine when the use of a FAb or F(Ab’)2 is a good fit for your specific research needs. And if your initiative calls for it, we can help you create and quality-check purified fragments for a variety of antibody species and isotypes.
The Advantages of Tailored Solutions
True to our fit-for-purpose operating model, we can tailor our methodology to your target molecule. We can provide:
-
Time savings through site-specific enzyme-cleavage reagents that can bind uniquely to the FAb and F(Ab’)2 fragments, purifying the fragment in a single step
-
Opportunities to more thoroughly and accurately measure monovalent vs. divalent binding to an antigen to characterize affinity, avidity, and epitope specificity. This may be especially useful for anti-idiotype antibody development, biodistribution studies, therapeutic antibody manufacturing applications, and more
-
The confidence that comes from applying our experience and expertise in digestion (Step One) and purification (Step Two) inn equal measures
-
The certainty that comes from quality control measures that confirm successful purification of FAb and F(Ab’)2 fragments, including non-reduced SDS-gel electrophoresis
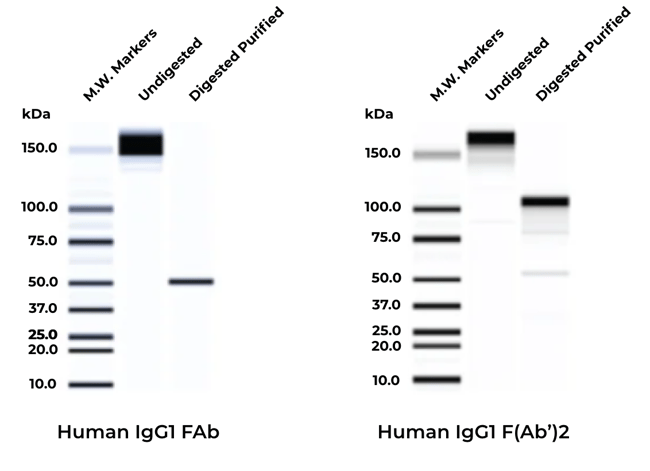
Non-reduced SDS-gels of whole IgG1 or affinity purified human IgG FAb (left) & F(Ab')2 (right). Whole human IgG was digested with the appropriate enzymes of FAb or F(Ab')2 and the fragments were then affinity purified from the digestion mixture. Appropriate molecular weights for the two fragments were obtained. Results may vary by species and isotype of the Ab.
Taking on the Tough Challenges Together
Many of our customers are apprehensive when it comes to traditional FAb and F(Ab’)2 fragment production, and that’s understandable. It’s commonly seen as a high-effort activity yielding uncertain outcomes. Low yields, highly inconsistent results across various species and isotypes, and questions about practical applicability leave many scientists wondering if FAb and F(Ab’)2 generation are really worth all the effort.
Relying on pepsin and papain for fragment generation frequently requires extensive optimization. Even then, purity might be low and the antigen-binding activity of the antibody may become compromised. Fragment generation from different species and isotypes often requires specialized procedures that come with a steep learning curve and a wide range of production and analysis techniques.
Related Resources

2 min read
AET2025 - Antibody Solutions Poster
How can antibody discovery programs efficiently interrogate – and yield antibodi...

12 min read
Reading the Biotechnology Tea Leaves: Therapeutic Antibody Developments in 2023 and 2024
With its “Antibodies to Watch” publication, The Antibody Society provides a comp...
14 min read
Looking Into the Future: Therapeutic Antibody Trends
Although Antibody Solutions focuses primarily on therapeutic antibody discovery ...
